Halal Investing 101: A Beginner’s Guide to Shariah-Compliant Investments

Investing can be an effective way of securing financial stability for you and your loved ones. Unfortunately, conventional forms of investing don’t always align with Islamic values of fairness, moderation, and social well-being. As a result, halal investing has become increasingly popular within and outside of the Muslim community.
You don’t have to be Muslim to participate in halal investments. Investors of various faiths view halal investing as an ethical form of generating wealth that not only benefits their finances, but also their communities. At the heart of halal investing is redirecting wealth into ethical ventures and divesting from social ills.
In this blog, we’ll discuss everything you need to know about halal investing including, what it is and guidelines to follow. We’ll also explore different types of halal investments, haram investments, and how to properly vet potential investment opportunities.
Table of contents
- What is halal investing?
- Halal investment guidelines
- Types of halal investments
- Types of haram investments
- How to evaluate halal investment options
- Understanding the benefits and risks of halal investing
- How zakat relates to your halal investments
- Final thoughts on halal investing
- Frequently asked questions
What is halal investing?
Halal investing is a form of ethical investing that complies with the way of Islam, also known as Shariah law. Shariah-compliant investments channel money into financial ventures that are in accordance with Islamic principles derived from the Qur’an, Hadith, and Sunnah.
The Qur'an is the divine word of God revealed to the Prophet Muhammad ﷺ. The Hadith are the collected sayings of the Prophet Muhammad ﷺ, while the Sunnah refers to his practices and those of his companions.
Contrary to the secular financial system, Islamic finance emphasizes socio-economic justice and mutually beneficial partnerships. As a result, you’ll find that Islamic investments encourage social responsibility and exhibit less risk. In Islam, individual financial rewards and societal well-being are not mutually exclusive. Both can, and should, co-exist.
Halal investment guidelines
Whether you’re a Muslim investing for the first time, or a seasoned investor curious about halal investing, there are four basic principles to keep in mind as a halal investor.
Focus on asset-based investments
In Islam, money is considered a medium of exchange that holds no intrinsic value in or of itself. Using money for the purpose of making money is considered haram, or not permissible. Money should never be the subject of investment, which makes most income-based investments, such as bonds and money market funds, haram.
Asset-based investments, such as real estate or fine art, focus on acquiring physical assets that hold intrinsic value. Returns on an asset-based investment are created through the appreciation of the asset’s value.
Investing in a small business is a great example of an asset-based investment. Businesses generate value through the provision of products and services. As a business grows, it becomes more valuable over time and generates investor returns in the short- and/or long-term. Stocks, technology, and precious metals are also considered asset-based investments.
Avoid riba (interest)
Another key tenant of halal investing is the prohibition of riba, or interest. In Arabic riba means “to increase,” or “to exceed.” Interest is considered haram because it implies excessive compensation without an appropriate value exchange.
Any profits derived from interest are considered riba because no intrinsic value is being provided. Investors are simply making money from having money to invest, which is counterintuitive to Islamic financial principles.
Interest-based investments, such as traditional mortgage loans, are considered exploitative because the rewards from such an investment are one-sided. The lender benefits exclusively from the borrower’s limited financial capability, while the borrower assumes the risk of potentially losing their home. This is considered an unequal distribution of risks and rewards.
Avoid prohibited industries
As mentioned above, acquiring businesses and stocks are asset-based investments that can be halal. However, there are certain industries that are considered haram. Goods and services that are harmful to the body, mind, soul, or society are prohibited.
The Qur’an and the Sunnah prohibit muslims from engaging in any form of oppression, sex outside of marriage, and consumption of toxic foods and beverages. As a result, halal investors should stay away from investment opportunities that require manufacturing, promoting, or selling the following goods and services:
- Alcohol
- Drugs
- Cigarettes
- Pornography
- Prostitution
- Gambling
- Pork
- Weapons
- Interest-bearing financial products
Avoid excessive risk and uncertainty
Lastly, halal investors should stay away from investments that come with excessive risk. High-risk investments are considered gharar, or uncertain. Gharar is derived from the Arabic word gharra which means “to deceive.” In order to preserve the integrity of the investment, transactions that lack transparency in terms, conditions, and/or payments should be avoided.
Determining whether or not an investment is gharar can be tricky. Every investor has a different risk-tolerance which influences their investment decisions. As a general rule of thumb, it’s best to stay away from:
- transactions with significant debt
- contracts with unclear clauses
- selling something you don’t own (short-selling)
- deferring the payment or delivery of goods to an unspecific future date
Additionally, any investment involving contracts where ownership of an asset(s) is dependent on future events is maisir, or speculation, and is considered haram.
Types of halal investments
If you’re new to halal investing you may think Shariah-compliant investors have limited opportunities. However, halal investing is quite versatile. There are plenty of investment vehicles you can use to create wealth as an ethical investor. The key is to accurately screen investment opportunities for haram activities. Take a look at some halal investment options, below.
Stocks
Purchasing stock allows you to acquire partial ownership in a corporation. Investors who purchase stock become shareholders in the company and as such, are entitled to a portion of the corporation’s profits and assets. Stock market investors generate profits from market capitalization, which represents the value of the company on the stock market. Stocks are considered halal as long as the industry in which the company operates in and its financial practices don’t violate Islamic law.
ETFs and Mutual Funds
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and mutual funds are investment vehicles that pool money from multiple investors to purchase a diversified portfolio of securities, such as stocks and bonds. ETFs can be traded throughout the day like individual stocks, while mutual funds are priced and traded only once per day after the market closes.
Since these funds hold a variety of assets, determining their Shariah compliance can be challenging. Zoya simplifies the process with its comprehensive ETF and mutual fund screener, which analyzes each fund's underlying holdings to provide a detailed breakdown of its Shariah compliance status.
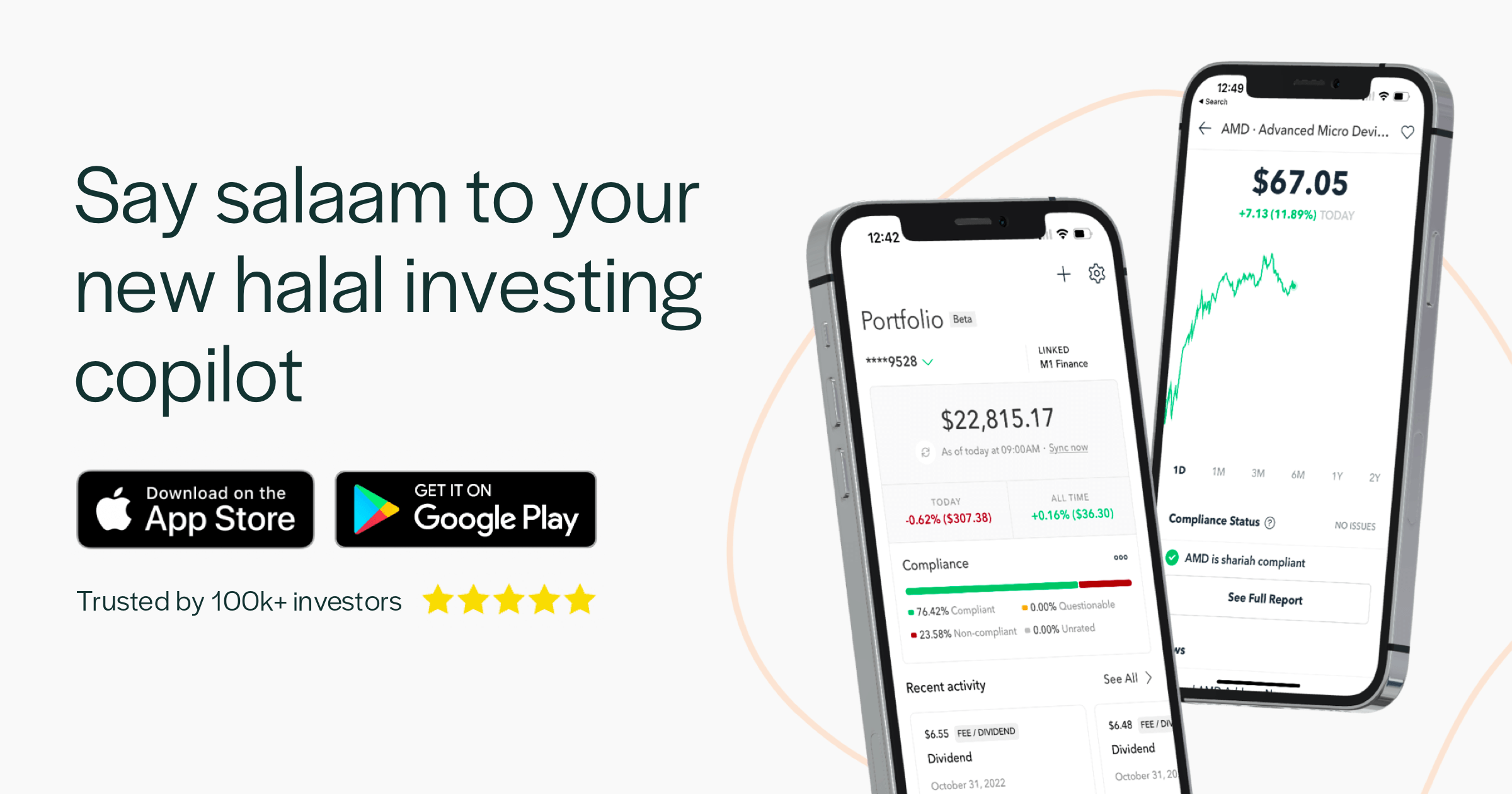
Zoya: Halal Investing App
Zoya makes halal investing easy by helping you build and monitor a shariah compliant investment portfolio with confidence and clarity.
Sukuks (Islamic bonds)
Sukuks are an Islamic variation of bonds that aren’t debt-based. Traditional bonds allow investors to profit off of interest, whereas sukuks allow investors to make money off of business profits.
Sukuks pool money from a group of investors and invest directly into a company. Instead of making money from interest, investors receive a fixed percentage of profits generated from the company’s business activities. Once the sukuk has matured, investors also receive their principal amounts back.
Real estate
Real estate is a tangible asset that holds intrinsic value and usually appreciates over time. Purchasing real estate is halal as long as interest-bearing loans aren’t used to acquire property or land. Islamic financial institutions offer mortgage loans free of interest for families and investors looking to purchase real estate.
Real estate investment trusts (REITs) are also viable investment options for halal investors who prefer a more hands off approach to real estate investing. Avoid REITs that are mortgage-based and prioritize REITs that generate most of their profits from rent.
Gold and precious metals
Investing in gold and precious metals is perhaps one of the oldest and most secure forms of investment. Similar to real estate, these commodities serve as a hedge against inflation and are useful beyond investment purposes. Owning and selling precious metals is completely halal as long as they are acquired and sold at a fair price.
Venture capital
Halal investors who have financial resources and specialized knowledge in one or more industries can participate in venture capital (VC) investing. Venture capital investors provide funds and guidance to startups, small businesses, and medium-sized businesses in exchange for equity. As partial owners, venture capital investors profit from business valuation and earnings, which is halal.
Crowdfunding
Crowdfunding pools small amounts of money from several investors for a specific company or project. This type of investment is usually done through an online platform. In exchange, investors receive equity shares in the company or project proportionate to their contribution. Crowdfunding makes sense for investors who are just starting out and want to minimize their risk.
Types of haram investments
There are some kinds of investments that are clearly haram because of how investment profits are generated. Halal investors should stay away from the following kinds of investments.
Bonds
Bonds are loans made by investors to corporations, governments, and other organizations for a defined period of time at a fixed interest rate. In addition to receiving their principal amount back at the date of maturity, investors receive regular interest payments in the meantime. Bonds are considered haram because investment profits are derived from interest.
Savings accounts
Traditional investors often deposit money into a high-yield savings account to passively generate investment income. High-yield savings accounts come with a certain annual percentage yield (APY) which represents the amount of interest you earn every year for holding your money in that account.
These investment vehicles are clearly haram due to their use of interest. In some cases, you may not even notice that your savings account is collecting interest. Opening a savings account at an Islamic banking institution is one way to steer clear of this issue.
Derivatives
A derivative is a financial contract whose value is determined by an underlying asset, or group of assets. Future contracts, binary options, forwards, and swaps are all examples of derivatives.
Derivatives are considered haram because they involve predicting whether the price of an asset will go up or down. According to Islamic law, derivatives present excessive risk, uncertainty, and speculation. As a result, they’re prohibited.
Forex
Foreign exchange trading is a form of online investment that involves trading currencies on a global decentralized market. Traders buy currencies while simultaneously selling others, requiring them to speculate on fluctuating exchange rates between currencies.
The majority view among Islamic scholars is that forex trading, particularly in the retail market, is not permissible. Several aspects of forex trading raise concerns from a Shariah perspective and are difficult to reconcile with the principles of Islamic finance. As such, halal investors are advised to avoid forex trading altogether.
How to evaluate halal investment options
Determining whether or not a potential investment opportunity is halal requires some due diligence. The two areas you should analyze are the industry in which the investment opportunity is located and its financial structure.
Identifying haram industries is pretty straightforward. However, since the concept of interest is embedded into the American financial system, halal investors need to pay special attention to how the returns on an investment are generated.
Investing has become increasingly decentralized through ventures such as forex, crowdfunding, and crypto. While this has lowered barriers to entry, it’s opened the way for new investment practices which need to be properly vetted.
Your safest bet is to lean towards investments with tangible assets. Investing in intangible assets can be halal, but they’ll need to be assessed for Shariah compliance.
Before investing in any venture, ask yourself the following questions:
- What kind of products or services does this company sell?
- Is this company known for unethical practices towards customers, clients, or employees?
- Where do my investment returns come from?
- Is there anything about this contract that is unclear?
Understanding the benefits and risks of halal investing
Halal investing offers unique benefits and challenges that appeal to a diverse range of investors.
Benefits of halal investing
- Disciplined approach: One of the primary advantages is its emphasis on a disciplined investment strategy. By adhering to Islamic principles, investors engage in rigorous research and continuous monitoring of securities, fostering informed decision-making.
- Conservative strategy: With an inherent focus on low debt, halal investing naturally adopts a conservative stance. This approach is particularly attractive to those who prefer to minimize their exposure to financial risk.
- Long-term focus: Unlike strategies that encourage frequent trading, halal investing discourages short-term speculation. This results in reduced portfolio turnover, which can lead to substantial cost savings in terms of fees and commissions. It also enhances tax efficiency by minimizing rapid transactions that could generate taxable capital gains.
Risks of halal investing
- Limited diversification: A significant challenge is the restricted pool of investment opportunities. The need to comply with Shariah guidelines narrows down the universe of potential investments. This limited diversity can increase the risk of loss, especially when certain market sectors are off-limits and cannot be capitalized on when they perform well.
- Sector exclusion: Halal investing prohibits involvement with specific sectors, like conventional financial services, which can limit potential gains when these segments of the market experience growth.
- Income restrictions: Islamic principles forbid earning interest, which may pose a challenge for managing cash reserves. This restriction means traditional methods like money market funds or interest-bearing accounts are off the table for generating income.
In summary, halal investing promotes a principled, thoughtful approach to building wealth. While it does limit certain sectors and income sources, these boundaries are part of what makes halal investing uniquely resilient and aligned with values that offer a structured framework for sustainable, long-term growth.
How zakat relates to your halal investments
Zakat, one of the five pillars of Islam, is an annual obligation to give 2.5% of your eligible wealth to those in need. While most Muslims are familiar with paying zakat on cash savings, calculating zakat on investments can be less straightforward.
In general, you'll need to consider the zakatable assets of the companies you're invested in, not just the market value of your shares. For stocks, this means looking at the company's current assets that would be eligible for zakat, such as cash, inventory, and receivables. Since you own a portion of these companies through your shares, you're responsible for zakat on your proportion of these zakatable assets.
Many investors find this calculation challenging, especially when dealing with stocks and ETFs. While some scholars allow using 25-30% of the market value as an estimate for zakatable assets, getting an accurate calculation is important. A quick and easy way to do this is through Zoya's zakat calculator. Just enter or import your holdings and it will automatically determine your zakat based on the latest financial data.
Incorporating zakat into your investment strategy not only fulfills a religious duty but also encourages a disciplined approach to halal wealth management. It helps you maintain a clear understanding of your financial standing and ensures that your wealth contributes positively to the broader community.
Final thoughts on halal investing
Halal investing offers a way to grow wealth while upholding Islamic principles. By focusing on asset-based investments, avoiding interest, steering clear of prohibited industries, and minimizing excessive risk, Muslims can confidently invest in line with their faith.
While navigating the investment landscape requires careful consideration, an increasing number of Shariah-compliant options are emerging. By taking the time to understand the key guidelines and properly vet opportunities, halal investors can find rewarding ways to secure their financial futures.
Ultimately, the decision of where and how to invest is a personal one that should be made after thorough research and consultation with qualified professionals. With the right approach, halal investing can be a powerful tool for growing wealth in an ethical manner.
Frequently asked questions about halal investing
Is investing in stocks halal (permissible) or haram (prohibited)?
Investing in stocks can be halal as long as the companies operate in permissible industries and follow Islamic financial principles like avoiding interest (riba). It's important to properly screen stocks for Shariah compliance.
What makes certain stocks haram (prohibited)?
Stocks in companies involved in prohibited activities like alcohol, gambling, pornography, etc. would be considered haram investments. Companies with excessive interest-based debt may also be screened out.
Is the stock market itself considered halal or haram?
The stock market as a whole is not inherently halal or haram. It's simply a marketplace to trade ownership stakes in companies. Each stock/company must be analyzed for Shariah compliance.
Do halal investment options only include stocks?
No, there are many other potential halal investments beyond stocks like real estate, precious metals, sukuk (Islamic bonds), REITs, crowdfunding, and venture capital - as long as they avoid riba (interest) and prohibited industries.
How can I find a list of Shariah-compliant halal stocks?
Zoya provides a powerful stock screener that analyzes companies based on business activities and financial ratios to identify halal stocks. Additionally, you can check the holdings of Shariah-certified ETFs as they typically publish their portfolio holdings on their websites, which contain pre-screened halal stocks.
What is the 5% rule in halal investing?
The 5% rule states that a company's revenue from impermissible (haram) sources must not exceed 5% of its total revenue to be considered Shariah-compliant. This is not an allowance but rather a tolerance level, as the goal is to avoid impermissible income entirely. Any impermissible portion should be purified through charitable giving.
Is stock trading the same as gambling?
Investing in stocks is fundamentally different from gambling. Investing involves purchasing ownership in real businesses with tangible value, while gambling creates artificial risk based on chance. Halal investing principles emphasize creating genuine value, not speculative quick gains.